Architecture
Overview
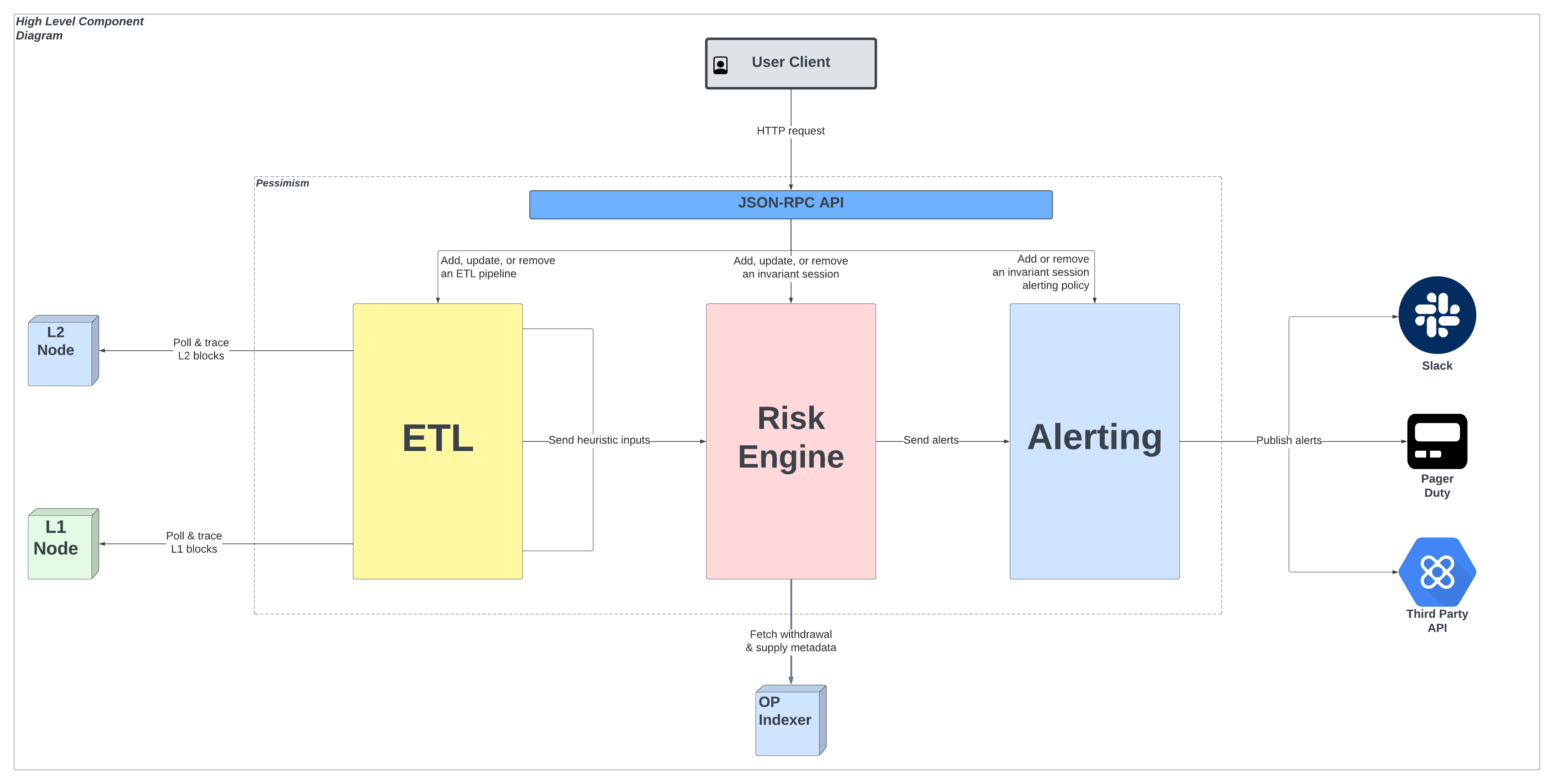
There are three subsystems that drive Pessimism’s architecture:
- ETL - Modularized data extraction system for retrieving and processing external chain data in the form of a DAG known as the Path DAG
- Risk Engine - Logical execution platform that runs a set of heuristics on the data funneled from the Path DAG
- Alerting - Alerting system that is used to notify users of heuristic failures
These systems will be accessible by a client through the use of a JSON-RPC API that has unilateral access to all three primary subsystems.
The API will be supported to allow Pessimism users via client to:
- Start heuristic sessions
- Update existing heuristic sessions
- Remove heuristic sessions
Diagram
The following diagram illustrates the core interaction flow between the three primary subsystems, API, and external data sources:
Shared State
To provide context about specific data values (ie. addresses to monitor) between subsystems, Pessimism uses a shared state store. The shared state store will be a non-persistent storage layer. This means that the data will not be persisted to disk and will be lost upon restart of the Pessimism service.
NOTE: As of now, the shared state store only supports an in-memory representation and fails to leverage more proper cache solutions like Redis